![[Warpspeed]](/home.gif)
![[Warpspeed]](/home.gif)
NULLFILE can either delete files, or protect sensitive data by overwriting it and then deleting it.
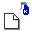
Usage: NullFile {Switches} File Spec <Drive Specs>
NULLFILE can either delete files, or overwrite sensitive data and then delete the files.
OS/2 when it deletes a file does not actually remove the data. It only removes the directory entry. NULLFILE physically overwrites the data area of the file. If you have many files to wipe all at the same time, try deleting them and using NULLDISK with the -e switch.
NULLFILE will scan all logical disk drives defined by the system, starting at drive A:. The drives are scanned in order, starting at A:, then B: and so on.
NULLFILE will remove the subdirectories which it is told to scan. By default NULLFILE only removes the files in the directories that it encounters. This switch forces NULLFILE to remove the directories as well.
This switch forces NULLFILE to erase the file to the US Department of Defence security specification DoD 5220.22-M. It writes over all of the data area of the file with 1's (FFh) then writes over it all again with 0's (00h). By default, it repeats this procedure 3 times. The optional n parameter for this test overrides the default repeat count of 3. Finally, the data area of the file is overwritten with the value of F6h.
NULLFILE will scan all logical disk drives defined by the system, starting at drive C:. The drives are scanned in order, starting at C:, then D: and so on.
NULLFILE, by default, wipes the file and then erases it. This switch will force NULLFILE to only erase (delete) the files. No wiping will occur.
By default, NULLFILE will not prompt you before it deletes files. Use this switch if you wish to be prompted before a file is wiped or deleted.
The default wipe count value is 1. This switch specifies a new repeat count. The repeat count is the number of times that the file is overwritten.
NULLFILE will include subdirectories as part of its search of the specified disk drives. If a subdirectory name is included as part of the file specification, then the search will include that subdirectory and all subdirectories below it. If no subdirectory is given as part of the file specification, then the current directory and all below it are included in the search.
The default value of the data which is written to the disk is zero (0). Use this switch to specify another number.
NULLFILEThis is not valid. A file specification must be supplied.
NULLFILE *.DOCNullFile will nullify all of the data in all .DOC files in the current directory.
NULLFILE *.WKS -HThis will instruct NullFile to nullify the contents of all .WKS files on all available hard disk drives.
NULLFILE D:\NullFile will wipe the contents of all files in the root directory of Drive D:.
NULLFILE D:\ /sNullFile will wipe the contents of all files on drive D:. The directory structures remain intact.
NULLFILE D:\ /snNullFile will delete all files on drive D:. The directory structures remain intact.
NULLFILE D:\ /SNDNullFile will delete all files on drive D:. The directory structures will be removed.